Duplicate content refers to content that appears online in more than one place. By “place,” we mean a page with a unique URL. It can be exactly the same content or almost exactly the same, and it can be on the same website or on another site.
You may not get penalized — technically — by Google for duplicate content, but it can hurt your search engine ranking. That’s because it’s hard for search engines to figure out which location of the content is the most relevant. As a result, none of the URLs end up ranking highly, and no single page gets the highest possible search visibility.
Google is supposed to be able to detect duplicate content, group all of the URLs into one cluster, and then choose the best result. But this doesn’t always work correctly, and the wrong URL may be chosen. Ultimately, website owners may notice lower rankings or reduced traffic due to duplicate content. Luckily, there are ways to prevent this sort of thing from happening to your sites.
Why Duplicate Content Is a Problem
Duplicate content impacts search engines and site owners in a number of ways:
- Search engines don’t know which URLs to include or not include in indexes.
- Search engines don’t know if link metrics (authority, trust, etc.) should be directed all to one page or to multiple pages.
- It’s unclear which URL to rank in SERPs (search engine results pages), and sometimes the undesirable URL can outrank the legit one.
- Link equity (the authority and value that one page passes to another) is diluted because other sites that want to include a backlink to the content have to choose between the multiple URLs. The link equity is then spread out across the duplicates instead of focusing on just one page.
Even with URLs that all direct to your website, if one has link attributes that make it look unfriendly to users, and Google ranks that version of the URL instead of the original, people may not want to click it. For example, yoursite.com/besttrails looks a lot more inviting than yoursite.com/besttrails/?utm_content=buffer&utm_medium=social. But if Google ranks the second one because it thinks that’s the primary version of the duplicate content, people won’t click it because it’s intimidating and untrustworthy-looking.
Also, the crawl “budget” of your website gets used up when you have duplicate content. Google crawls websites to find new content, and Google also re-crawls sites periodically to see if there’s anything new. If you have duplicate content on your site, that means it’ll take more time to thoroughly crawl all of the pages. That can lead to a slower timetable for Google to index and re-index pages and show them in search results.
Google’s Duplicate Content Policy
Duplicate content on a site is not grounds for action on that site unless it appears that the intent of the duplicate content is to be deceptive and manipulate search engine results.
However, while Google doesn’t penalize website owners for most instances of duplicate content, the company goes on to say:
In the rare cases in which Google perceives that duplicate content may be shown with intent to manipulate our rankings and deceive our users, we’ll also make appropriate adjustments in the indexing and ranking of the sites involved. As a result, the ranking of the site may suffer, or the site might be removed entirely from the Google index, in which case it will no longer appear in search results.
What might Google consider an intent to deceive users and/or manipulate search engine rankings? Intentionally making domains, subdomains, and pages with duplicate content. Also, publishing scraped content — especially if you don’t add anything else of value to it.
Remember this, though: Even if Google won’t officially penalize you or consider your duplicate content malicious, it can still hurt your SEO efforts. If Google has stopped ranking your site due to duplicate content issues, you can submit a reconsideration request once the problems have been fixed.
How Duplicate Content Happens
Usually, a website owner won’t purposely create duplicate content. That’s why Google doesn’t penalize it too drastically. That’s also the difference between copied content and duplicate content.
Copied content is when you take the exact wording from another website and publish it on your own. Duplicate content is when you accidentally or unknowingly have another version of your own content somewhere else online.
Here, we’ll go over common ways duplicate content ends up online. After that, we’ll talk about how to solve the problem of duplicate content.
HTTP, HTTPS, WWW, and Non-WWW Pages
If your site has two different versions — www.yoursite.com and yoursite.com, for example – the same content will be on both versions of the site, which means there’s duplicate content. The same is true for http:// and https:// sites.
Pagination
Pagination can happen when one article or the comments section of a blog post spans multiple pages. Or, maybe there’s a gallery of images with each one on a separate page. This sort of duplication can also happen on a page with infinite scroll, where new content populates as the user keeps scrolling down.
URL Variations
URL parameters, like tracking codes, can unintentionally create duplicate content. For example, a page on your website may be yoursite.com/sneakers, but if you have a tracking code to see where people clicked through from, it could look like yoursite.com/newsletter?utm_source=newsletter. Even if Google and other search engines don’t consider this duplicate content, you may have to deal with the separate parameters creating multiple entries in your analytics platforms, too.
Session IDs can have the same effect. A session is a short history of what a visitor does on a website, like when they add something to their shopping cart. The session remains when the person clicks through to other pages so that their cart remains intact. The session ID is the unique modifier for that session, and it’s sometimes stored in the URL (yoursite.com?sessionId=jow8082345hnfn8456). This can create multiple different URLs with the same page content.
The same can happen if you have a printer-friendly version or mobile-friendly version of the content. Search engines will think there are multiple pages of the same content. Because…there are.
This is also a common occurrence on e-commerce websites, particularly when users filter search results. The URL stays just about the same, but with an addendum at the end, like the size or color. This is called faceted or filtered navigation. The content on the pages is nearly the same, but the URLs are unique.
Even trailing slashes can make a URL unique. For example, yoursite.com/page and yoursite.com/page/. The quickest way to see if this is causing a duplicate content issue is to go to both versions of a page. If one doesn’t load, you don’t have to worry about it. Otherwise, redirection is an option (more on that in a bit).
More Ways Duplicate Content Happens
- E-Commerce Product Descriptions: It’s common for different e-commerce sites to have duplicate content when using the manufacturer’s description of a product.
- Image Attachment Pages: When each image attachment has a separate page, this can create duplicate content.
- Search Results Pages: These add a parameter to the search URL, like yoursite.com?q=search-term.
- Staging Environment: This is a duplicate version of your site used for testing.
- Tag and Category Pages: When you use a tag or category, WordPress will automatically create dedicated tag and category pages. This can sometimes cause duplicate content when one page has multiple categories or tags.
How to Fix Duplicate Content
Depending on which WordPress SEO plugin you are using, you will find settings that will help you address most of the smaller issues listed above. For example, in the Yoast plugin, you can disable attachment page URLs for images:
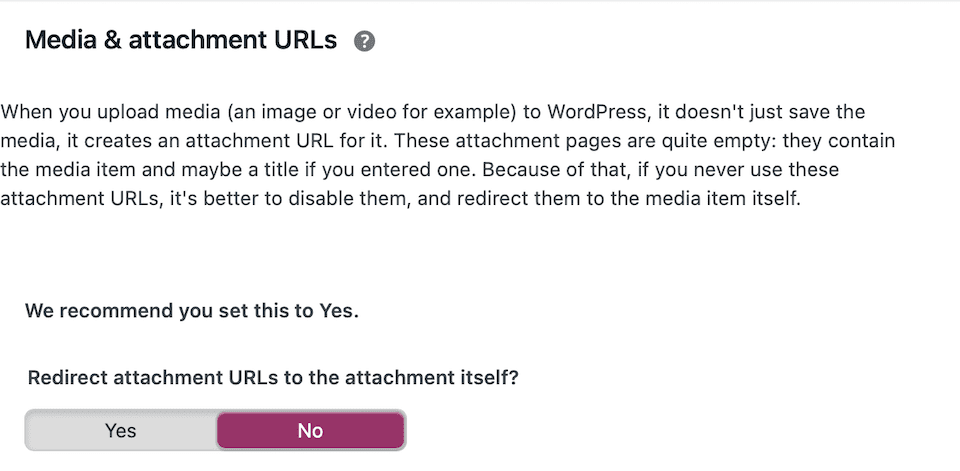
WordPress also has a built-in option for turning off comment pagination:
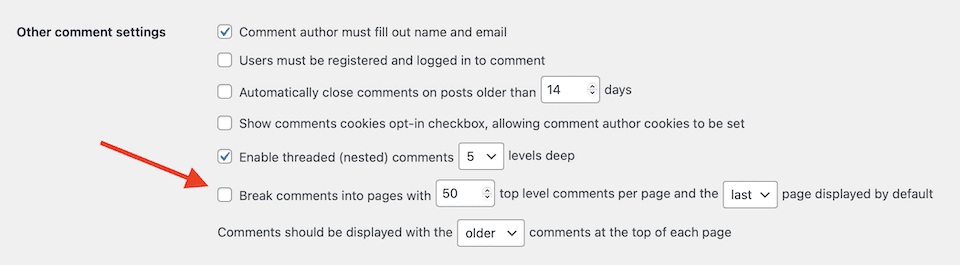
Otherwise, though, the following practices are the main ways to solve duplicate content issues.
1. Find the Duplicate Content
First, you have to find instances of duplicate content. Tools like the Ahrefs Site Audit and the Google Search Console can crawl your site and let you know if there are any duplicate content warnings.
If you’re trying to find duplicate content on your site for a specific keyword, you can type this into Google:
site:yoursite.com intitle: keyword
You’ll then see all of the pages on your website that include that keyword. A good rule of thumb is to search for a specific keyword so that it’s easier to comb through the results.
If you think there’s a particular article that’s been duplicated elsewhere online, you can use a plagiarism checker like Grammarly or Copyscape to find other instances of exact-match sentences. Or, you can paste a full sentence or two into Google to see if it shows up somewhere other than on your site.
2. Adjust the Content’s URL through Canonicalization
Once you know there’s duplicate content online, it’s time to determine which page is the main one to keep.
You canonicalize that primary page for search engines. Canonicalization tells search engines that a URL is a master version of a page — that this page should appear in search results instead of any duplicates the engine may run across. Here are two ways to canonicalize content:
301 Redirect
Create a 301 redirect from the duplicate page(s) to the main page. You can use a redirection plugin to do this. The duplicate pages will stop competing with one another, and the main page will become more popular and relevant, which means it will start to rank higher. We have an article about how to create redirects with WordPress to help you out.
You also gain the added benefit of any link juice/page authority from the redirected URL being transferred to the new target, too.
Rel=”canonical” Attribute
This attribute lets search engines know that a page is a copy of a URL, and that any links, metrics, and ranking power should be applied to the specified main URL, not the copied page. The attribute should be included in the HTML head of each duplicate page with a link to the original page you want the focus on. Google has documentation that goes in-depth about how to add the attribute, and we have more detailed content on canonical URLs and WordPress to supplement that.
To avoid content scraping, which is when bots copy, download, and repost your website content, add the rel=”canonical” attribute to your own web pages. The attribute will be self-referential — it’ll point to the URL that it’s currently on. Even if the content does get scraped, so long as the bots port the complete HTML code, your version will still be considered the original.
3. Adjust Your Domain URLs Using the Google Search Console
The Google Search Console lets you designate your website’s preferred domain, like yoursite.com instead of www.yoursite.com, for example. You can also let Googlebot know how to handle different URL parameters. This may clear up some or all of your duplicate content issues. But with Google only. Not with other search engines. Platforms such as Bing and Yandex have their own webmaster tools.
More Tips for Preventing or Fixing Duplicate Content
- When adding internal links, use the same version of the domain, whether that’s with or without www, for example. Also always use the same version of a page with or without a trailing slash. It doesn’t matter which structure you choose, but be consistent with it.
- If you’re arranging for syndicated content, the website that’s using the content should add a backlink to the original content. Not a variation of the URL. But the original, main, canonical URL.
- Don’t publish empty pages as placeholders. Each empty page will be indexed, which can make the search engine think you have a lot of duplicate content.
- Reduce how much similar content you have. For example, let’s say you have a legal website and you cater to different counties in your area. Each county-specific page may include similar information if you’re talking about the same law topic, like personal injury law. One option is to merge the page into a larger one about both counties, or you can vary the content more to keep the pages separate.
Final Thoughts About Duplicate Content
Coming across a small amount of duplicate content isn’t usually cause for concern. But technical issues that are impacting hundreds or thousands of pages do need to be dealt with. Plus, it won’t hurt to clear up any and all duplicate content issues. That’s just part of running an uncluttered and high-performing site. After all, the last thing you want to do is compete with yourself and ruin your own ranking because of content you have total control over.
Once you have duplicate content figured out, you may also want to check out our article about how to handle keyword cannibalization to prevent duplicate keyword issues.
How have you managed to deal with duplicate content on your sites? Let’s talk about real-world strategies in the comments!
Article featured image by NikAndr / shutterstock.com





I read a lot of articles on the internet regarding SEO but the way you explained everything is quite impressive. In addition to this, I experienced content added on the sidebar and footer also count as duplicate content. Excited to know your version on this. By the way, thanks for explaining the duplicate content problem in short.
Duplicacy of content sometimes creates a problem and we are unaware that our web pages contain duplicate content. Thanks for sharing important information to fix duplicate content.